Identification and Functional Characterization of Upregulated Hub Genes in Adenocarcinoma across Multiple Organ Sites
Download
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to identify and characterize key hub genes involved in adenocarcinoma progression across multiple organ types via integrative bioinformatics analysis.
Methods: Gene expression datasets from GEO and GEPIA2 were analyzed to identify genes whose expression was upregulated across various adenocarcinoma types. Protein‒protein interaction networks were constructed, and hub genes were identified. Transcription factors and microRNA regulatory networks were mapped, and functional enrichment analysis was performed.
Results: Ten hub genes (CHEK1, CDC20, ANLN, RRM2, CCNB1, CCNA2, KIF23, TOP2A, BUB1, and KIF11) were consistently overexpressed in six adenocarcinoma types and linked to cell cycle regulation and mitotic progression. In prostate adenocarcinoma, five of these genes were not significantly overexpressed. Survival analysis revealed that most hub genes were associated with poorer survival. Regulatory network analysis identified key transcription factors (e.g., TP53 and MYC) and miRNAs (e.g., hsa-miR-103a-3p and hsa-let-7e-5p) as modulators of these genes.
Conclusions: This integrative approach identified critical hub genes and regulatory networks involved in adenocarcinoma progression, offering potential avenues for targeted therapies and emphasizing the importance of personalized strategies for different adenocarcinoma subtypes.
Introduction
Adenocarcinoma, a malignant tumor originating from glandular epithelial cells, is a prevalent form of cancer affecting various organs, including the lungs, colon, pancreas, and prostate [1]. This type of cancer accounts for approximately 40% of all lung cancers and is the most common histological subtype of colorectal cancer [2, 3]. The incidence of adenocarcinoma has been steadily increasing worldwide, posing a significant global health challenge [4].
The molecular pathogenesis of adenocarcinoma involves complex genetic and epigenetic alterations that disrupt normal cellular processes, leading to uncontrolled cell growth and division [5]. Key molecular events in adenocarcinoma development include mutations in oncogenes such as KRAS, EGFR, and BRAF, as well as inactivation of tumor suppressor genes such as TP53 and CDKN2A [6, 7]. These genetic alterations result in the dysregulation of critical signaling pathways, including the MAPK/ERK, PI3K/AKT, and Wnt/β-catenin pathways, which contribute to tumor initiation, progression, and metastasis [8].
Advances in molecular profiling techniques, particularly next-generation sequencing, have significantly enhanced our understanding of the genomic landscape of adenocarcinoma [9]. This knowledge has led to the identification of numerous potential therapeutic targets and the development of targeted therapies. For example, EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have shown remarkable efficacy in treating EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma, whereas BRAF inhibitors have demonstrated promising results in BRAF V600E-mutant colorectal adenocarcinoma [10, 11].
Despite these advancements, several challenges remain in the management of adenocarcinoma. First, the heterogeneity of these tumors, both inter- and intratumorally, complicates treatment strategies and contributes to drug resistance [12]. Second, while targeted therapies have shown initial success, many patients eventually develop resistance, necessitating the identification of new therapeutic targets and combination strategies [13]. Third, early detection of adenocarcinoma remains challenging, particularly for organs such as the pancreas, where symptoms often appear only in advanced stages [14].
Furthermore, our understanding of the complex interplay between genetic alterations, epigenetic modifications, and the tumor microenvironment in adenocarcinoma progression is still incomplete [15]. Additionally, the role of noncoding RNAs, such as long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) and microRNAs (miRNAs), in regulating gene expression and contributing to adenocarcinoma development is an emerging area of research that requires further investigation [16]. Moreover, integrating gene expression data with other omics data, such as proteomics and metabolomics data, could offer a more holistic understanding of adenocarcinoma biology and guide personalized treatment approaches [17].
This study aims to address these challenges through a comprehensive, integrative bioinformatics approach to identify and characterize key hub genes and regulatory networks that may serve as universal drivers of adenocarcinoma progression across various organ sites. While previous studies have explored hub genes related to cell cycle regulation within specific adenocarcinomas, this research uniquely contributes by identifying common hub genes and regulatory networks consistent across multiple adenocarcinoma types. By analyzing gene expression profiles from multiple datasets (GEO and GEPIA2), constructing protein-protein interaction (PPI) networks, and identifying transcription factors and miRNAs modulating these hub genes, our study not only strengthens the reliability of these identified targets but also enhances the understanding of their regulatory mechanisms.
The identification of universally overexpressed hub genes and their regulatory networks across adenocarcinomas in the lung, colon, pancreas, and more can provide new avenues for developing broad-spectrum therapeutic targets. Moreover, these findings may pave the way for the use of these genes as biomarkers, potentially applicable across diverse adenocarcinoma subtypes, aiding early diagnosis, prognosis, and the development of tissue-agnostic therapies. This comprehensive profiling of adenocarcinoma aims to bridge critical gaps in our understanding of adenocarcinoma biology and addresses the urgent need for more effective, personalized, and universally applicable treatment strategies.
Materials and Methods
Our study employed a comprehensive bioinformatics approach to identify and analyze upregulated hub genes in adenocarcinoma across multiple organ sites. The methodology consisted of several key steps:
Data collection and differential gene expression analysis
To identify upregulated hub genes in adenocarcinoma, we conducted differential gene expression analysis using datasets from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) and GEPIA2 databases. Three adenocarcinoma studies from GEO: GSE32863, [18] GSE10972, [19] and GSE15471 [20, 21], were selected for analysis. The criteria for identifying upregulated genes were set to a log fold change (logFC) greater than 0 and an adjusted p value less than 0.05. FunRich software (http://www.funrich.org/) was used to identify genes commonly upregulated across all three datasets.
In parallel, we performed differential gene expression analysis via GEPIA2 [22] across five different types of adenocarcinomas: colon (COAD), lung (LUAD), pancreas (PAAD), rectum (READ), and stomach (STAD) adenocarcinoma. For this analysis, the threshold was set to a logFC greater than 1 and an adjusted p value less than 0.05. These parameters align with standard practices in gene expression studies, providing a well- justified selection that reduces noise while capturing genes most relevant to adenocarcinoma progression. The Venn diagram web tool from https://bioinformatics.psb. ugent.be/webtools/Venn/ was employed to identify genes commonly upregulated across all five adenocarcinoma types.
Integration and Integration and protein‒protein interaction (PPI) network construction
We cross-referenced gene expression findings from GEO and GEPIA2 databases to further ensure that identified genes and interactions were consistent across multiple sources, which helps to counteract potential dataset-specific biases. Thus, the intersection of the gene sets obtained from the GEO and GEPIA2 analyses was determined via FunRich. The intersecting genes (129 in total, see supplementary material) were then used to construct a protein‒protein interaction (PPI) network via StringDB [23] as follows: genes were uploaded to the server and an interaction confidence score threshold of 0.7 was selected for the network construction, as well as eliminating disconnected genes. This threshold was selected to ensure high-confidence interactions while avoiding overly restrictive parameters that might exclude relevant connections. Thus, maintaining a balanced choice between a strong yet interpretable network, including only interactions with biological significance. The resulting PPI network was imported into Cytoscape [24] for further analysis.
Hub gene identification
Within Cytoscape, the CytoHubba [25] plug-in was utilized to identify the top ten hub genes on the basis of two key metrics: degree centrality and betweenness centrality. This dual approach of using both degree centrality and betweenness centrality ensured that the hub genes identified were not only highly connected but also central to the overall network structure, reflecting their potential significance in adenocarcinoma.
To validate the expression levels of the identified hub genes in adenocarcinoma, we conducted secondary verification using the GEPIA2 database. This step confirmed the consistency of the hub genes’ upregulation across multiple datasets and provided further support for their relevance in adenocarcinoma. Survival analysis was also performed for the hub genes, using overall survival in months with an adjusted p value of 0.05 and a median cutoff.
miRNA and Transcription Factor Target Prediction
The validated hub genes were then submitted to MirWalk [26] to predict miRNAs that target these genes. To increase the reliability of the predictions, only miRNAs that were validated by three major databases, TargetScan [27], miRDB [28], and miRTarBase [29], all available within MirWalk, were considered. The requirement of validation in three databases increases specificity, reducing the risk of false positives. Our threshold for miRNA-target inclusion required evidence in all three databases to ensure that predicted interactions are biologically meaningful, given the complexity of miRNA regulation. The expression levels of the identified miRNAs across different cancer types were further analyzed via the OncoMir database [30].
For transcription factor (TF) analysis, we employed the TRRUST v2 database [31], which includes experimentally validated transcriptional regulatory interactions. We used the search function to find key regulators for submitted query genes, the hub genes in our case. This database was chosen due to its stringent curation, ensuring that only validated TF-target relationships were included. By using validated TF data, we aim to improve the reliability of our regulatory network predictions.
Functional enrichment analysis
Hub genes and TFs were submitted to GeneTrail [32] to perform functional enrichment analysis, focusing on molecular functions and biological processes from the Gene Ontology knowledgebase [33, 34], as well as Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways.
Construction of the Regulatory Network
Finally, we integrated the hub genes, their target miRNAs, and transcription factors into a comprehensive regulatory network. This network was constructed via StringDB and visualized via Cytoscape, providing a detailed map of the molecular interactions and regulatory pathways involved in adenocarcinoma.
This methodological approach ensured the identification of the most consistently upregulated hub genes in adenocarcinoma, along with their associated regulatory elements, providing a robust framework for further investigation into their roles in cancer development and progression.
Results
Identification of Upregulated Genes in Adenocarcinoma
Through differential gene expression analysis, we identified 875 upregulated genes that were common across the three GEO datasets (GSE32863, GSE10972, and GSE15471; Figure 1 in the supplementary material).
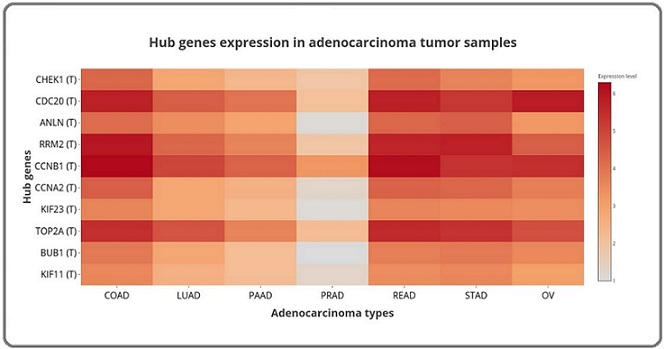
Figure 1. Heatmap of Hub Gene Expression Levels Across Different Adenocarcinoma Types. This heatmap illustrates the expression levels of key hub genes identified in adenocarcinoma across various tumor samples. The hub genes are listed on the y-axis, including CHEK1, CDC20, ANLN, RRM2, CCNB1, CCNA2, KIF23, TOP2A, BUB1, and KIF11. The different types of adenocarcinoma are represented on the x-axis: COAD (colon adenocarcinoma), LUAD (lung adenocarcinoma), PAAD (pancreatic adenocarcinoma), PRAD (prostate adenocarcinoma), READ (rectum adenocarcinoma), STAD (stomach adenocarcinoma), and OV (ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma). The data is log2 (TPM + 1) transformed and only tumor data is employed. Detailed box plots with significance values are provided in the supplementary materials. Color Gradient: The color gradient represents the expression levels of these genes, with darker shades of orange and brown indicating higher expression levels, and lighter shades indicating lower expression levels. Key Insights: The heatmap reveals that most of these hub genes are consistently overexpressed across the various adenocarcinoma types, with some variability in expression levels. Notably, PRAD (prostate adenocarcinoma) exhibits lower expression levels for certain hub genes such as CCNA2, KIF23, and BUB1, which aligns with previous findings indicating that these genes are not significantly overexpressed in PRAD compared to other adenocarcinoma types. This visualization highlights the potential significance of these hub genes in the progression of adenocarcinoma and underscores their relevance as potential therapeutic targets or biomarkers across different adenocarcinoma subtypes.
Similarly, in the GEPIA2 analysis, 471 upregulated genes were found to be common across five adenocarcinoma types (COAD, LUAD, PAAD, READ, and STAD; Figure 2 in the supplementary material). The intersection of these two gene sets yielded 129 genes that were consistently upregulated across both sources (Figure 3 in the supplementary material).
Figure 2. Survival Map Across Different Adenocarcinoma Types. The map shows the log10-transformed hazard ratios (HR) for hub genes CHEK1, CDC20, ANLN, RRM2, CCNB1, CCNA2, KIF23, TOP2A, BUB1, and KIF11 across six adenocarcinoma types (COAD, LUAD, PAAD, READ, STAD, and OV) and prostate adenocarcinoma (PRAD). The methods are overall survival in months, with a significance level (FDR) of 0.05 and a median group cutoff. Positive log10 (HR) values (in red) indicate that higher gene expression is associated with worse survival, while negative values (in blue) suggest improved survival. The highlighted cells indicate statistical significance .
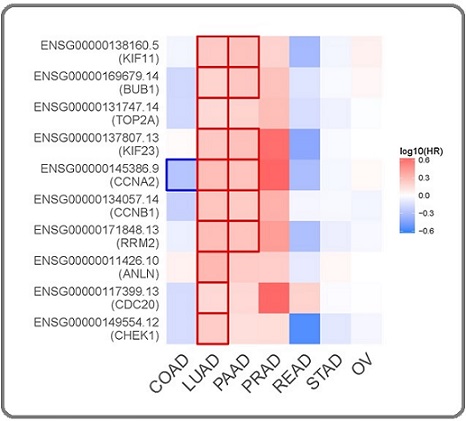
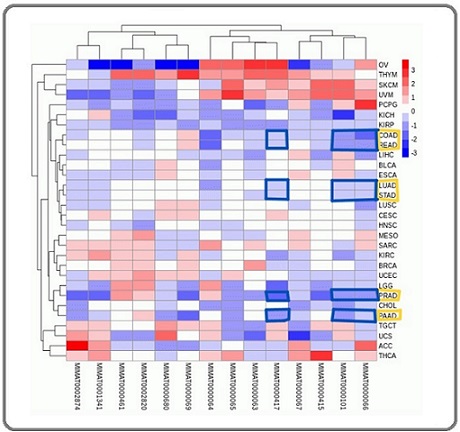
Figure 3. Heatmap of miRNA Expression Across Various Cancer Types. This heatmap visualizes the expression levels of identified miRNAs (labeled with their corresponding MIMAT IDs) across a wide range of cancer types (adenocarcinoma types are boxed in yellow on the right). The hierarchical clustering is based on average miRNA expression levels, with mean-based scaling of expression values within samples. The color scale represents the relative expression levels, with red indicating upregulation, blue indicating downregulation, and white indicating neutral expression levels. Highlighted in blue boxes are specific adenocarcinoma types, including COAD (colon adenocarcinoma), READ (rectum adenocarcinoma), LUAD (lung adenocarcinoma), STAD (stomach adenocarcinoma), PRAD (prostate adenocarcinoma), and PAAD (pancreatic adenocarcinoma). These boxed regions show consistent downregulation across these adenocarcinoma types of miRNAs hsa-miR-103a-3p, hsa-let-7e-5p, and hsa-miR-15b-5p. The hierarchical clustering along the top and left axes groups the miRNAs and cancer types based on similarity in expression profiles, revealing patterns of miRNA dysregulation that may be characteristic of specific cancer types, including adenocarcinomas. This analysis underscores the potential role of these miRNAs as biomarkers or therapeutic targets in adenocarcinoma.
Construction and Analysis of the PPI Network
The protein‒protein interaction (PPI) network constructed from these 129 common genes included 500 edges and 129 nodes, with an average degree of 7.75 and an average local clustering coefficient of 0.41. The network exhibited a significant PPI enrichment P value of less than 1.0e-16, indicating that the identified genes are more interconnected than would be expected by chance, suggesting a prominent level of functional association among them.
Identification of Hub Genes
Using CytoHubba in Cytoscape, we identified ten hub genes within the PPI network on the basis of degree and betweenness centrality metrics: CHEK1, CDC20, ANLN, RRM2, CCNB1, CCNA2, KIF23, TOP2A, BUB1, and KIF11. These hub genes were found to be significantly overexpressed in six adenocarcinoma types (COAD, LUAD, PAAD, READ, STAD, and ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma (OV)). However, in prostate adenocarcinoma (PRAD), the genes KIF11, KIF23, CCNA2, ANLN, and BUB1 were not significantly overexpressed. Figure 1 shows the general heatmap, and detailed boxplots for each gene, with significance annotations, are provided in the supplementary material. The survival analysis results are presented in Figure 2.
Regulatory network involving transcription factors and miRNAs
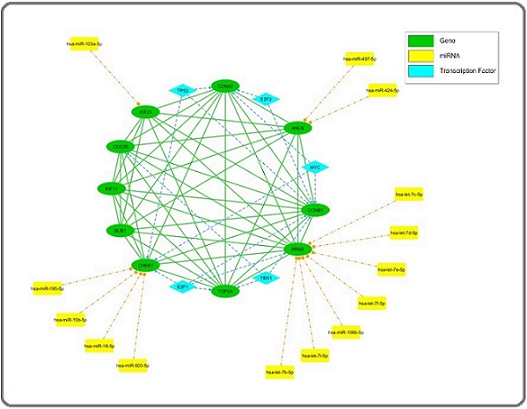
We further explored the regulatory landscape of these hub genes by identifying key transcription factors and miRNAs that target them. The transcription factors identified include YBX1, E2F1, MYC, E2F3, and TP53. The miRNAs targeting these hub genes include hsa-miR-503-5p, hsa-miR-106b-5p, hsa-miR-16-5p, hsa-miR-103a-3p, hsa-let-7b-5p, hsa-let-7c-5p, hsa-let- 7d-5p, hsa-let-7e-5p, hsa-let-7f-5p, hsa-let-7i-5p, hsa- miR-15b-5p, hsa-miR-195-5p, hsa-miR-424-5p, and hsa-miR-497-5p. Among these, the miRNAs hsa-miR- 103a-3p, hsa-let-7e-5p, and hsa-miR-15b-5p were consistently downregulated across all adenocarcinoma types in the Oncomir database (COAD, READ, LUAD, STAD, PRAD, and PAAD) (Figure 3). The integrated regulatory network comprising hub genes, TFs, and miRNAs is presented on Figure 4.
Figure 4. Regulatory Network of Hub Genes, Transcription Factors, and miRNAs in Adenocarcinoma. This figure illustrates the complex regulatory network involving the identified hub genes, transcription factors (TFs), and miRNAs in adenocarcinoma. The network consists of: -Hub Genes (Green Ovals): The core hub genes identified in the study, including CHEK1, CDC20, ANLN, RRM2, CCNB1, CCNA2, KIF23, TOP2A, BUB1, and KIF11. These genes are central to the protein-protein interaction (PPI) network and are significantly overexpressed in various adenocarcinoma types. -Transcription Factors (Blue Diamonds): Key TFs targeting the hub genes, such as YBX1, E2F1, MYC, E2F3, and TP53, are shown to regulate the expression of these critical genes. These TFs play a crucial role in controlling cell cycle progression and other cancer-related processes. - miRNAs (Yellow Rectangles): The miRNAs predicted to target the hub genes include hsa-miR-503-5p, hsa-miR-106b-5p, hsa-miR-16-5p, hsa-miR-103a-3p, hsa-let-7b-5p, hsa-let-7c-5p, hsa-let-7d-5p, hsa-let-7e-5p, hsa-let-7f-5p, hsa-let-7i-5p, hsa-miR-15b-5p, hsa-miR-195-5p, hsa-miR-424-5p, and hsa-miR-497-5p. These miRNAs are shown to interact with multiple hub genes, suggesting their potential role in fine-tuning the expression of genes critical for adenocarcinoma progression. The network highlights the intricate interactions between these molecular players, where transcription factors regulate the hub genes, and miRNAs further modulate their expression. This multi-layered regulatory framework underscores the complexity of gene regulation in adenocarcinoma and points to potential therapeutic targets for disrupting key pathways involved in tumor growth and progression .
Functional enrichment analysis
Functional enrichment analysis of the 129 common upregulated genes revealed significant enrichment in several biological processes and pathways relevant to adenocarcinoma. The most prominent categories included cell cycle regulation, mitotic regulation, mitotic nuclear division, cellular senescence, and G1 to S cell cycle control (Figures 5 and 6).
Figure 5. Top 10 Most Enriched Gene Ontology (GO) Biological Process Categories in Up-Regulated Hub Genes in Adenocarcinoma. This bar chart displays the top 10 most significantly enriched Gene Ontology (GO) biological process (BP) categories associated with the upregulated hub genes and transcription factors identified in adenocarcinoma. The categories are ranked based on the -log10(p value), indicating the statistical significance of enrichment. -Enriched Categories (Red Bars): The chart highlights that the most enriched biological processes are primarily related to the regulation of the cell cycle, mitotic processes, and cellular organization. Specifically, categories such as "regulation of cell cycle," "regulation of mitotic cell cycle," and "regulation of mitotic nuclear division" are strongly represented, reflecting the crucial role of cell cycle control in the pathogenesis of adenocarcinoma. -Key Insights: The prominence of these categories underscores the importance of dysregulated cell cycle processes in adenocarcinoma development and progression, suggesting that the identified hub genes play central roles in driving tumor cell proliferation and survival through these pathways. This analysis provides a deeper understanding of the biological functions most affected by the upregulated genes in adenocarcinoma, offering potential targets for therapeutic intervention.
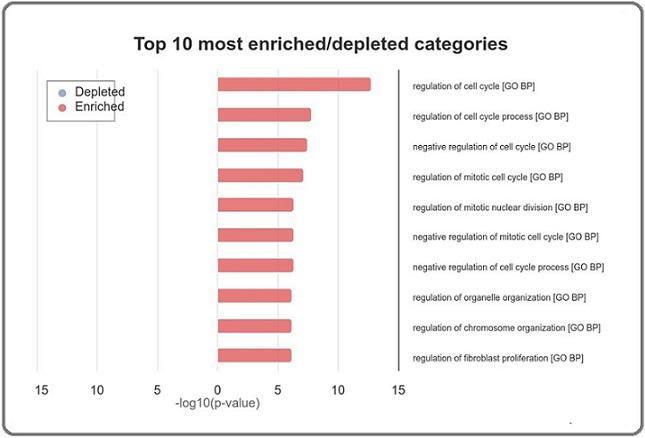
Figure 6. Top 10 Most Enriched Pathway Categories in Up-Regulated Hub Genes in Adenocarcinoma. This bar chart depicts the top 10 most significantly enriched pathway categories associated with the upregulated hub genes identified in adenocarcinoma. The categories are ranked by the -log10 (p value), reflecting the statistical significance of the enrichment. -Enriched Categories (Red Bars): The analysis reveals that the most enriched pathways are closely related to cell cycle regulation, DNA damage response, and cellular senescence. Specifically, categories such as "Retinoblastoma Gene in Cancer," "Cell Cycle" (from both WikiPathways and KEGG), "Cellular Senescence," and "G1 to S cell cycle control" are prominently featured, indicating their critical role in the pathogenesis of adenocarcinoma. -Key Insights: These enriched pathways suggest that dysregulation of cell cycle checkpoints, failure of cellular senescence mechanisms, and aberrant DNA damage response are central to the development and progression of adenocarcinoma. The pathways related to the retinoblastoma gene and miRNA regulation of DNA damage response also highlight potential molecular targets for therapeutic intervention in adenocarcinoma. This enrichment analysis underscores the importance of these pathways in driving the malignant behavior of adenocarcinoma cells, offering insights into potential areas for further research and drug development .
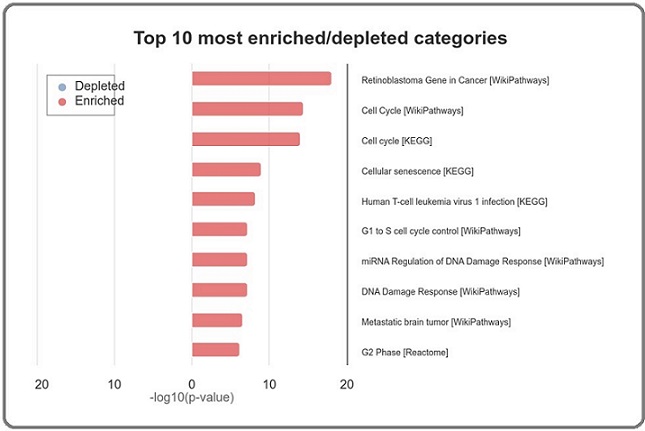
These findings suggest that the identified hub genes play critical roles in the control of cell proliferation and survival, key processes in the pathogenesis of adenocarcinoma.
These results provide a comprehensive overview of the molecular mechanisms underlying adenocarcinoma, highlighting key regulatory networks and potential targets for therapeutic intervention.
Discussion
Subtype-Specific Variability and Implications for Hub Genes as Biomarkers
This study conducted a comprehensive analysis of upregulated genes across multiple adenocarcinoma types to identify key hub genes and their associated regulatory networks. The findings underscore the critical roles of cell cycle regulation, mitotic processes, and the DNA damage response in adenocarcinoma progression, highlighting these pathways as promising therapeutic targets.
While ten hub genes (CHEK1, CDC20, ANLN, RRM2, CCNB1, CCNA2, KIF23, TOP2A, BUB1, and KIF11) were identified as consistently overexpressed across various adenocarcinomas, we acknowledge the significant heterogeneity inherent to these cancers. Each adenocarcinoma subtype is shaped by distinct molecular drivers and microenvironmental factors. For instance, prostate adenocarcinoma (PRAD) is heavily influenced by androgen receptor signaling, while colorectal adenocarcinoma is often characterized by aberrant Wnt/β-catenin pathway activation and mismatch repair deficiencies [35]. These subtype-specific molecular landscapes may modulate the relevance of these hub genes to tumorigenesis and progression.
The finding that five hub genes (e.g., CCNA2, KIF23, and BUB1) are not significantly overexpressed in PRAD underscores this variability. Although these genes have broad potential as biomarkers or therapeutic targets, their utility is not uniform across all subtypes. This observation reinforces the necessity for subtype-specific studies to validate and refine the roles of these hub genes in adenocarcinoma progression.
Clinical Implications of Identified Hub Genes and Regulatory Networks
Despite the variability, the consistent overexpression of the ten hub genes across six adenocarcinoma types (colon [COAD], lung [LUAD], pancreatic [PAAD], rectal [READ], stomach [STAD], and ovarian [OV]) suggests their pivotal roles in driving adenocarcinoma progression. Their mechanisms, primarily related to cell cycle regulation and mitotic processes, make them compelling targets for therapeutic intervention. For example, CHEK1 and CCNB1 regulate crucial cell cycle checkpoints that are frequently dysregulated in cancers. Similarly, CDC20, identified as a key mitotic regulator, has shown promise as a therapeutic target [36], with inhibitors such as Apcin demonstrating preclinical antitumor effects. Our findings support the rationale for further exploration of these compounds in adenocarcinoma models and clinical trials. Survival analysis further corroborated the prognostic significance of these genes. Hub genes such as CCNB1, BUB1, and CDC20, which are associated with poorer survival outcomes, emerge as potential oncogenic drivers and therapeutic candidates. However, the absence of a consistent pattern in PRAD highlights the complexity of cancer biology and the necessity for personalized therapeutic approaches tailored to each subtype’s unique molecular characteristics.
The regulatory network analysis identified transcription factors (e.g., TP53, MYC) and miRNAs (e.g., hsa-miR-103a-3p, hsa-let-7e-5p) that modulate these hub genes. These findings open new avenues for RNA-based therapies or small molecule modulators targeting these regulatory elements. For instance, combining such targeted approaches with existing treatments could enhance efficacy and help overcome drug resistance.
The consistent downregulation of specific miRNAs across adenocarcinomas suggests their potential as noninvasive biomarkers. For example, liquid biopsy platforms measuring miRNAs such as hsa-miR-103a-3p could enable early detection and monitor treatment response, ultimately improving outcomes through personalized management strategies.
Pathways Underlying Subtype-Specific Differences
Pathways enriched in this study, such as cell cycle regulation and mitotic progression, are foundational to many cancers. However, their activation may vary in magnitude and context across subtypes. For instance, the DNA damage response pathway, associated with CHEK1 and CDC20, may be particularly critical in subtypes with high genomic instability, such as pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Similarly, the regulatory interplay of miRNAs and transcription factors likely varies between subtypes, influencing the expression and impact of these hub genes in different contexts.
Clinical and Research Challenges
Adenocarcinoma heterogeneity presents challenges for developing universal biomarkers and therapeutic strategies. To address this, future studies should integrate tissue-specific genomic, epigenomic, and transcriptomic data to elucidate context-dependent roles of these genes. Advances such as single-cell sequencing and spatial transcriptomics can further unravel intratumoral heterogeneity, clarifying the operation of hub genes in diverse cellular microenvironments [37].
Our findings suggest that while hub genes may not serve as universal biomarkers, they can inform a multifaceted approach to adenocarcinoma management. Genes such as CCNB1 and CDC20, associated with poor survival across subtypes, could be prioritized for broad-spectrum therapeutic targeting. Conversely, genes such as ANLN and KIF11 may require tailored strategies reflecting subtype-specific expression patterns and regulatory mechanisms.
Limitations and Future Directions
Recognizing adenocarcinoma subtype variability enhances the interpretation of our findings. Although this study identifies potential universal patterns, the heterogeneity of adenocarcinomas necessitates nuanced validation and application. Future research should focus on validating hub gene functionality in specific subtypes and exploring subtype-targeted therapies. Integrating broad-spectrum analyses with subtype-specific validation will advance the development of biomarkers and treatments aligned with adenocarcinoma’s diverse biological landscapes.
The methodology employed to identify hub genes is robust and integrative, combining GEO and GEPIA2 datasets to minimize bias and maximize reliability. However, publicly available datasets inherently vary in sample preparation and processing, which may introduce variability. Despite these challenges, the procedural rigor, including the use of stringent thresholds and cross-validation, ensures confidence in the identified hub genes.
Experimental validation is a critical next step to confirm the functional roles of these hub genes and regulatory elements. Specific approaches include:
1. Functional Validation: Use CRISPR-Cas9 knockouts or RNAi in adenocarcinoma cell lines to elucidate the roles of key hub genes, such as CHEK1, CDC20, and CCNB1, in tumor progression.
2. Pathway Inhibition Studies: Test small molecule inhibitors targeting cell cycle regulators (e.g., CDC20 inhibitors like Apcin) in cell and animal models.
1. miRNA Modulation: Investigate the functional impact of miRNAs (e.g., hsa-let-7e-5p, hsa-miR-103a-3p) through mimics or inhibitors, assessing their effects on hub gene expression and cancer cell behavior.
2. In Vivo Models: Develop mouse or patient-derived xenograft (PDX) models to study the physiological impact of modulating these genes and pathways.
In conclusion, this study identifies key hub genes and regulatory networks consistently overexpressed across multiple adenocarcinoma types, highlighting their roles in cancer progression. While primarily correlative, our findings provide a robust foundation for future experimental research. The identified genes and pathways, such as cell cycle regulation and DNA damage response, represent viable starting points for understanding and targeting adenocarcinoma biology.
Future work should prioritize experimental validation and explore subtype-specific applications to bridge bioinformatics-driven insights with therapeutic innovation. These efforts will advance precision oncology and improve clinical outcomes across the diverse spectrum of adenocarcinomas.
Author contributions
Ricardo Romero: Conceptualization (Lead), Data curation (Equal), Formal analysis (Equal), Investigation (Lead), Methodology (Lead), Writing – original draft (Lead), Writing – review \& editing (Lead).
Dulce Bastida: Data curation (Equal), Formal analysis (Equal), Investigation (Supporting), Methodology (Supporting), Writing – review \& editing (Supporting).
Data availability statement
The data that support the findings of this study are openly available in public databases cited in the text.
Financial disclosure
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for- profit sectors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
References
- Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL , Torre LA , Jemal A. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians.2018;68(6). CrossRef
- International association for the study of lung cancer/american thoracic society/european respiratory society international multidisciplinary classification of lung adenocarcinoma Travis WD , Brambilla E, Noguchi M, Nicholson AG , Geisinger KR , Yatabe Y, Beer DG , et al . Journal of Thoracic Oncology: Official Publication of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer.2011;6(2). CrossRef
- Colorectal cancer Brenner H, Kloor M, Pox CP . The Lancet.2014;383(9927). CrossRef
- Cancer statistics, 2020 Siegel RL , MillerKD , Jemal A. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians.2020;70(1). CrossRef
- Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation Hanahan D, Weinberg RA . Cell.2011;144(5). CrossRef
- Comprehensive molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network . Nature.2014;511(7511). CrossRef
- Cancer genome landscapes Vogelstein B, Papadopoulos N, Velculescu VE , Zhou S, Diaz LA , Kinzler KW . Science (New York, N.Y.).2013;339(6127). CrossRef
- Oncogenic Signaling Pathways in The Cancer Genome Atlas Sanchez-Vega F, Mina M, Armenia J, Chatila WK , Luna A, La KC , et al . Cell.2018;173(2). CrossRef
- Cancer transcriptome profiling at the juncture of clinical translation Cieślik M, Chinnaiyan AM . Nature Reviews. Genetics.2018;19(2). CrossRef
- Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma Mok TS T, Wu Y, Thongprasert S, Yang C, Chu D, Saijo N, Sunpaweravong P, et al . The New England Journal of Medicine.2009;361(10). CrossRef
- Encorafenib, Binimetinib, and Cetuximab in BRAF V600E-Mutated Colorectal Cancer Kopetz S, Grothey A, Yaeger R, Van Cutsem E, Desai J, Yoshino T, Wasan H, et al . The New England Journal of Medicine.2019;381(17). CrossRef
- Tumour heterogeneity and resistance to cancer therapies Dagogo-Jack I, Shaw AT . Nature Reviews. Clinical Oncology.2018;15(2). CrossRef
- A view on drug resistance in cancer Vasan N, Baselga J, Hyman DM . Nature.2019;575(7782). CrossRef
- Early detection of pancreatic cancer Pereira SP , Oldfield L, Ney A, Hart PA , Keane MG , Pandol SJ , Li D, et al . The Lancet. Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2020;5(7). CrossRef
- Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis Quail DF , Joyce JA . Nature Medicine.2013;19(11). CrossRef
- The Role of Non-coding RNAs in Oncology Slack FJ , Chinnaiyan AM . Cell.2019;179(5). CrossRef
- Multi-omics approaches to disease Hasin Y, Seldin M, Lusis A. Genome Biology.2017;18(1). CrossRef
- Genome-scale analysis of DNA methylation in lung adenocarcinoma and integration with mRNA expression Selamat SA , Chung BS , Girard L, Zhang W, Zhang Y, Campan M, Siegmund KD , et al . Genome Research.2012;22(7). CrossRef
- DACT3 is an epigenetic regulator of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in colorectal cancer and is a therapeutic target of histone modifications Jiang X, Tan J, Li J, Kivimäe S, Yang X, Zhuang L, Lee PL , et al . Cancer Cell.2008;13(6). CrossRef
- Combined gene expression analysis of whole-tissue and microdissected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma identifies genes specifically overexpressed in tumor epithelia Badea L, Herlea V, Dima SO , Dumitrascu T, Popescu I. Hepato-Gastroenterology.2008;55(88).
- Regulation of actin-binding protein ANLN by antitumor miR-217 inhibits cancer cell aggressiveness in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma Idichi T, Seki N, Kurahara H, Yonemori K, Osako Y, Arai T, Okato A, et al . Oncotarget.2017;8(32). CrossRef
- GEPIA2: an enhanced web server for large-scale expression profiling and interactive analysis Tang Z, Kang B, Li C, Chen T, Zhang Z. Nucleic Acids Research.2019;47(W1). CrossRef
- The STRING database in 2023: protein-protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest Szklarczyk D, Kirsch R, Koutrouli M, Nastou K, Mehryary F, Hachilif R, Gable AL , et al . Nucleic Acids Research.2023;51(D1). CrossRef
- Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS , Wang JT , Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B, Ideker T. Genome Research.2003;13(11). CrossRef
- cytoHubba: identifying hub objects and sub-networks from complex interactome Chin C, Chen S, Wu H, Ho C, Ko M, Lin C. BMC systems biology.2014;8 Suppl 4(Suppl 4). CrossRef
- miRWalk: An online resource for prediction of microRNA binding sites Sticht C, De La Torre C, Parveen A, Gretz N. PloS One.2018;13(10). CrossRef
- The biochemical basis of microRNA targeting efficacy McGeary SE , Lin KS , Shi CY , Pham TM , Bisaria N, Kelley GM , Bartel DP . Science (New York, N.Y.).2019;366(6472). CrossRef
- miRDB: an online database for prediction of functional microRNA targets Chen Y, Wang X. Nucleic Acids Research.2020;48(D1). CrossRef
- miRTarBase update 2022: an informative resource for experimentally validated miRNA-target interactions Huang H, Lin Y, Cui S, Huang Y, Tang Y, Xu J, Bao J, et al . Nucleic Acids Research.2022;50(D1). CrossRef
- OncomiR: an online resource for exploring pan-cancer microRNA dysregulation Wong NW , Chen Y, Chen S, Wang X. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England).2018;34(4). CrossRef
- TRRUST v2: an expanded reference database of human and mouse transcriptional regulatory interactions Han H, Cho J, Lee S, Yun A, Kim H, Bae D, Yang S, et al . Nucleic Acids Research.2018;46(D1). CrossRef
- GeneTrail 3: advanced high-throughput enrichment analysis Gerstner N, Kehl T, Lenhof K, Müller A, Mayer C, Eckhart L, Grammes NL , et al . Nucleic Acids Research.2020;48(W1). CrossRef
- Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium Ashburner M., Ball C. A., Blake J. A., Botstein D., Butler H., Cherry J. M., Davis A. P., et al . Nature Genetics.2000;25(1). CrossRef
- The Gene Ontology knowledgebase in 2023 Aleksander SA , Balhoff J, Carbon S, Cherry JM , Drabkin HJ , Ebert D, Feuermann M, et al . Genetics.2023;224(1). CrossRef
- The cancer genome atlas research network: a sight to behold Giordano TJ . Endocrine Pathology.2014;25(4). CrossRef
- Targeting Cdc20 as a novel cancer therapeutic strategy Wang L, Zhang J, Wan L, Zhou X, Wang Z, Wei W. Pharmacology & Therapeutics.2015;151. CrossRef
- Application of Cell-free DNA Analysis to Cancer Treatment Corcoran RB , Chabner BA . The New England Journal of Medicine.2018;379(18). CrossRef
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright
© Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Biology , 2025
Author Details