The Application of Antioxidant in Skin Cancer Research: A Bibliometric Study
Download
Abstract
Objective: Skin cancer is one of the most common malignancies globally. Considering the potential therapeutic benefits of antioxidants, this study aims to examine the trends and patterns in antioxidant application within skin cancer research over the past three decades.
Methods: A bibliometric analysis was conducted on 990 English-language articles published between 1990 and 2025, retrieved from the Scopus database. Data were processed using Bibliometrix (R-based) and VOSviewer to assess publication trends, research productivity, collaboration networks, keyword co-occurrence, and thematic evolution in antioxidant-related skin cancer research.
Result: The annual growth rate of publications reached 11.42%, with a sharp rise in output post-2010. The United States and China were the most productive countries, while European countries demonstrated strong international collaboration. Frequently recurring subjects included apoptosis, cancer, oxidative stress, and antioxidants. Co-occurrence analysis identified four major clusters: (1) cell biomolecular mechanisms, (2) drug metabolism, (3) malignancy agents, and (4) pharmacological innovation. Highly cited articles emphasized molecular mechanisms of antioxidants in tumor suppression. Thematic evolution showed a transition from mechanistic studies to translational and clinical research.
Conclusion: Antioxidant-related research in skin cancer is rapidly evolving, with increasing global contributions and thematic diversification. This study provides a comprehensive overview of current knowledge and identifies key research gaps, including the underexploration of areas such as DNA repair, tumorigenesis, and lesser-studied antioxidant compounds, as well as the limited translation of mechanistic findings into clinical applications.
Introduction
Skin cancer remains one of the most common cancers globally, with over 1.5 million new cases diagnosed annually, accounting for a significant portion of cancer statistics [1]. Melanoma causes around 57,000 deaths each year, while non-melanoma skin cancers, including basal and squamous cell carcinoma, are rising, especially among older populations [2]. Existing treatments such as surgery, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy have their limitations, including adverse effects, recurrence, and growing drug resistance [3]. This situation highlights the urgent need to explore adjuvant strategies that can enhance treatment efficacy. One promising avenue is the use of antioxidants, which can counteract oxidative damage and potentially improve patient outcomes.
Interest in antioxidants as complementary cancer therapies has increased significantly. Research indicates that natural compounds like curcumin, epigallocatechin gallate, and resveratrol can inhibit tumor growth and induce apoptosis in skin cancer cells [4, 5]. For example, Wei et al. found that combining curcumin with 5-fluorouracil significantly enhances cytotoxicity and reverses drug resistance, suggesting a synergistic effect [6]. Furthermore, antioxidant-based adjuvants also help reduce treatment-induced oxidative stress and inflammation, which are key factors in tumor progression and recurrence [7]. Given their therapeutic benefits and low toxicity, antioxidants are promising candidates for integration into cancer treatment.
Antioxidants primarily exert their anticancer effects by modulating oxidative stress, a central process in UV-induced skin cancer development. Reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are elevated due to UV exposure and inflammation, can cause DNA damage, destabilize the genome, and promote tumor growth [7]. Natural antioxidants help neutralize excess ROS, restore redox balance, and downregulate inflammatory pathways such as NF-κB and MAPK [4]. Many also induce intrinsic apoptosis through mitochondrial regulation and upregulate tumor suppressors like p53 [5]. These actions can reduce cancer cell viability and improve sensitivity to conventional treatments. Thus, incorporating antioxidants may enhance treatment outcomes both biologically and clinically.
Given this increased interest, mapping the research landscape is crucial to identify trends, knowledge gaps, and influential contributions. This study uses bibliometric analysis as a systematic tool to evaluate global research output on antioxidants as adjuvant therapies for skin cancer. By utilizing Scopus and VOSviewer, it analyzes publication trends, citation networks, and keyword co- occurrences over time [8]. This approach provides a comprehensive overview of how the scientific community is addressing this emerging field, allowing for the identification of the most studied compounds, leading institutions, and research hotspots. Ultimately, this bibliometric evidence supports informed directions for future experimental and clinical work.
Materials and Methods
Study Design
Bibliometric analysis is a structured and methodical approach widely applied across disciplines to synthesize and integrate research findings centered around a particular theme or research question [9]. This approach is crucial in expanding and refining knowledge within the examined field. Just like other forms of literature reviews, bibliometric studies generally follow a four-phase process: (i) defining relevant search keywords, (ii) collecting and compiling research outputs into a dataset, (iii) summarizing the extracted data, and (iv) performing analytical evaluation of the results [10]. The stages of this process are illustrated in Figure 1, based on the frameworks proposed by Sanchez-Sánchez et al. (2024) and Altarturi et al. (2020) [10, 11].
Figure 1. Workflow of Bibliometric Analysis Phases.
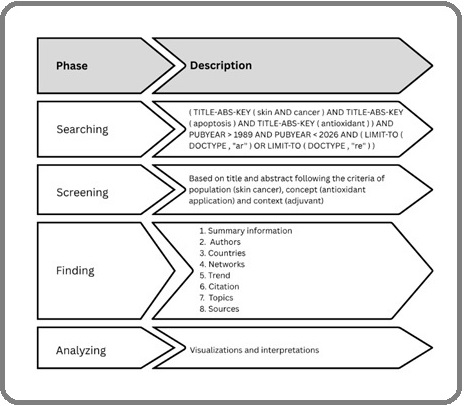
Additionally, the BIBLIO checklist serves as the reporting guideline for bibliometric reviews, particularly in biomedical research [12].
Database and Search Strategy
Scopus (www.scopus.com) and Web of Science (webofscience.com) are two of the most extensively utilized databases for conducting bibliometric literature searches [13]. Scopus, in particular, is recognized as the largest abstract and citation database of peer-reviewed literature, offering comprehensive global coverage across diverse disciplines including science, technology, medicine, social sciences, and the arts and humanities [14]. It indexes over 20,000 peer-reviewed journals from publishers such as Elsevier, Emerald, Informs, Taylor & Francis, Springer, and Interscience [13]. To ensure that the overview of the growing research landscape on antioxidant application in skin cancer treatments is inclusive, Scopus was selected as the primary data source for this bibliometric study. The database search was conducted on June 6, 2025.
The following keywords were used to find relevant publications: “skin and cancer,” “apoptosis”, and “antioxidants.” No restrictions were applied regarding their publication years, and only sources written in English were included. The selection criteria did not limit the research methodologies used in the included articles. While the primary goal was to capture the broad thematic patterns in research on antioxidant application in skin cancer treatments, applying this approach within bibliometric analysis poses challenges as a result of the title-based screening limitations. The retrieved Scopus data were exported in comma-separated values (CSV) format.
Data Collection
Initially, the data were screened by the first reviewer, where studies were assessed based on their titles and abstracts. The inclusion criteria used during this stage focused on the population (skin cancer), the concept (antioxidant application), and the context (adjuvant). The second reviewer independently verified the screening results, and any discrepancies between the team members were resolved through discussion during a research meeting. Following the completion of the screening process, the dataset was reconverted into a CSV file using a software called R-Studio to enable further analysis.
Data Analysis
The data were analyzed using R Base version 4.5.0 in conjunction with R-Studio version 4.5.0 (Posit, Massachusetts, USA) [15]. along with VOSviewer version 1.6.19 developed by the Centre for Science and Technology Studies in the Netherlands [16]. Within the R environment, the open-source packages Bibliometrix and Biblioshiny were utilized. The latter functions as a web-based graphical interface for the Bibliometrix package, enabling the extraction of key bibliometric metrics [13, 15]. These metrics include descriptive data, annual publication output, top contributing authors, most prolific journals, most cited documents, keyword analysis, conceptual structure mapping, and thematic trend analysis. The Bibliometrix suite has been widely adopted across various scientific fields for bibliometric evaluations. Meanwhile, VOSviewer was employed in this study to construct and visualize the bibliometric maps, providing graphical representations of co-authorship, keyword co-occurrence, and citation networks [16].
Results
General information
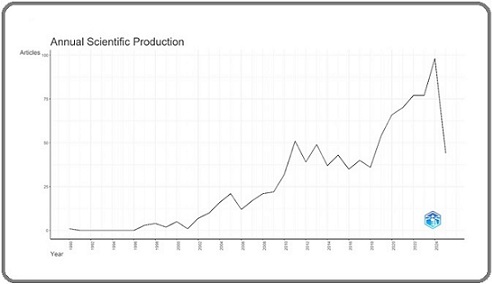
A comprehensive search through the Scopus database resulted in a total of 1,001 records. The screening process was carried out as per the population, concept, and context frameworks. As part of the filtering process, 11 entries were excluded for being published in languages other than English. After applying the inclusion criteria, 990 articles were identified and included in the bibliometric analysis. The initial output from Biblioshiny was a summary of key bibliometric statistics about the dataset. To comprehensively explore the literature surrounding antioxidant application in skin cancer treatments, it was essential to employ a broad analytical approach. The dataset covered publications from 1990 to 2025, encompassing 483 distinct journals and contributions from 4,795 authors, with 10.3% of them being solo-authored works. The included articles referenced nearly 483 sources, and the average number of citations per document was 74.5 %. Over 57% of the total documents were articles. In addition, the dataset comprised 423 review articles. The significant proportion of articles relative to other publication types suggested that the field of antioxidant application in skin cancer treatments was well-established and of high academic relevance.
Pattern of publication
This section explores the annual growth trends in the number of publications related to antioxidant application in skin cancer treatments. The analysis showed that publication volume steadily increased over time, with an average annual growth rate of 11.42%, as presented in Table 1.
| Item | Results |
| Main information | |
| Timespan | 1990-2025 |
| Sources (Journal, Books, etc) (n) | 483 |
| Documents (n) | 990 |
| Annual Growth Rate (%) | 11.42 |
| Document average age (mean) | 8.32 |
| Average citation per document (mean) | 74.5 |
| Authors | |
| Authors | 4,795 |
| Authors of single-authored docs | 50 |
| International co-authorship (%) | 26.06 |
| Co-author per document | 5.73 |
| Content | |
| Keywords Plus | 11,375 |
| Author’s Keywords | 2,401 |
| Document types | |
| Article | 567 |
| Review | 423 |
Although there were notable declines in output during certain years, such as 2001, 2006, and 2016, the overall trajectory remained upward. A marked acceleration in scholarly activity was observed between 2011 and 2023, culminating in a peak during 2024, when nearly 100 articles were published. In contrast, the earliest recorded publication in 1990 received the lowest citation rate, averaging only 0.39 citations. The highest average citation rate was recorded in 2006, with 27.27 citations per article. Overall, the field produced an average of 28.28 articles per year, with each article receiving approximately 6.38 citations annually.
This section also assessed research outputs by countries. Each publication was attributed to the corresponding author’s country, allowing evaluation of both single-country publications (SCP) and multiple-country publications (MCP) [13]. The ratio of international collaboration was calculated by dividing MCP by the total number of publications for each country, providing a clearer picture of inter-country research cooperation in this field.
The analysis found that the United States led in terms of research outputs, contributing 149 articles, followed closely by China with 142 articles. India and Iran occupied the third and fourth positions with 134 and 47 articles, respectively, reflecting a noticeable productivity gap. Among the ten most productive countries, six demonstrated considerable international collaboration. Based on their MCP ratios, these included Poland (32.0%), Italy (30.8%), Spain (30.4%), Korea (27.5%), Iran (25.5%), and the United States (25.5%). These findings underscore the widespread international attention and collaborative engagement surrounding antioxidant-based strategies in skin cancer research.
Authors and sources
Various bibliometric indicators assessed an author’s scientific productivity and impact, including their publications, citation counts, h-index, g-index, and fractional authorship scores. Although some scholars argue that publication volume alone does not accurately reflect an individual’s influence in a field, this analysis identified Hasan Mukhtar as the most prolific contributor to the topic, with nine published articles. Another leading author was Rajesh Agarwal, who has eight publications. In bibliometric evaluation, each author or co-author is credited with a proportional share of citations from the articles they contribute to. The concept of article fractionalization distributes credit equally among co- authors by assigning each a score equivalent to the inverse of the total number of contributors per article. Using this method, Rajesh Agarwal emerged with the highest fractional authorship score of 2.63, followed by Hasan Mukhtar with 2.27.
The analysis also examined citation metrics, particularly the total number of citations each publication had accumulated since its release. Importantly, the works of Baur, Williams, Clement, and Yang ranked among the most cited in this research domain, each surpassing 1,000 citations globally. Interestingly, nine of the ten most-cited articles were published before 2010, with only one released in 2012, potentially indicating a shift in research focus over time. One prominent example is the 2006 article by Baur et al., which has garnered nearly 3,500 citations, almost twice the number of the second- most-cited article [17]. The most frequently cited papers are summarized in Table 2, offering a comprehensive overview of the most influential studies in the field.
| Rank | Author(s) | Year | Title of Paper | Journal | Citation | Total Citation per Year |
| 1 | Baur JA, et al. [17] | 2006 | Therapeutic potential of resveratrol: the in vivo evidence | Nat Rev Drug Discov | 3,576 | 178.8 |
| 2 | Williams RJ, et. Al. [18] | 2004 | Flavonoids: antioxidants or signaling molecules? | Free Radic Biol Med | 1,915 | 87.05 |
| 3 | Clement CH, et al. [19] | 2012 | ICRP Statement on Tissue Reactions and Early and Late Effects of Radiation in Normal Tissues and Organs – Threshold Doses for Tissue Reactions in a Radiation Protection Context | Ann ICRP | 1,072 | 76.57 |
| 4 | Yang CS, et al. [20] | 2009 | Cancer prevention by tea: animal studies, molecular mechanisms and human relevance | Nat Rev Cancer | 1,031 | 60.65 |
| 5 | López-Lázaro M. [21] | 2009 | Distribution and Biological Activities of the Flavonoid Luteolin | Mini-Rev Med Chem | 960 | 56.47 |
| 6 | Bickers DR, et al. [22] | 2006 | Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of Skin Disease | J Invest Dermatol | 931 | 46.55 |
| 7 | Srinivasan M, et al. [23] | 2007 | Ferulic Acid: Therapeutic Potential Through Its Antioxidant Property | J Clin Biochem Nutr | 899 | 47.32 |
| 8 | Yang CS, et al. [24] | 2002 | Inhibition of Carcinogenesis by Tea | Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol | 867 | 36.13 |
| 9 | Pandi-Perumal SR, et al. [25] | 2006 | Melatonin: Nature's most versatile biological signal? | Febs J | 848 | 42.4 |
| 10 | Ichihashi, et al. [26] | 2003 | UV-induced skin damage | Toxicology | 846 | 36.78 |
Regarding publication venues, the International Journal of Molecular Sciences emerged as the most frequently used outlet for studies on antioxidant applications in skin cancer, having published 35 articles. Other frequently selected journals included Frontiers in Pharmacology, Molecules, Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy, and Food and Chemical Toxicology.
Subject Area
The themes explored in the reviewed publications were highly relevant, in line with the main objective of this bibliometric study, i.e., to identify publication trends related to the use of antioxidants in skin cancer research. An in-depth analysis of the literature content based on author keywords and abstracts was conducted to achieve this. Reviewing abstracts offered valuable perspectives on the evolving research direction and helped identify gaps in current knowledge. Understanding these thematic trends was crucial for evaluating the potential and direction of future research in this field. Since most of the highly cited publications were published before 2010, they likely reflected previously prioritized topics that might have evolved since then. Therefore, the thematic analysis was focused on the literature published from 2010 onwards (Figure 2).
Figure 2. Annual Growth of Publications on Antioxidant in Skin Cancer Research.
Among the most recent themes identified were those related to skin aging, with six publications addressing this topic between 2023 and 2024 (Figure 3).
Figure 3. Trends in Emerging Topics and Frequently Addressed Themes in Antioxidant-Based Skin Cancer Research.
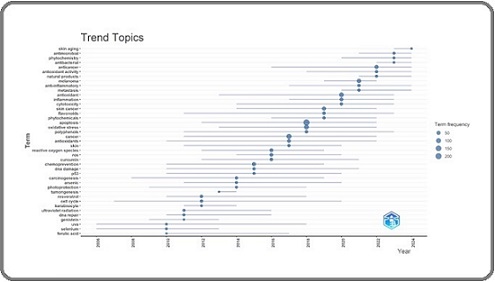
The key recurring subjects in the context of antioxidant application in skin cancer treatments included apoptosis (211 articles), cancer (116 articles), oxidative stress (91 articles), and antioxidant (89 articles). The most frequently used keywords were “apoptosis” (1,971 instances), “cancer” (1,098 instances), “oxidative stress” (800 instances), and “antioxidant” (753 instances). Other less frequently appearing terms included “chemoprevention,” “reactive oxygen species,” and “skin cancer.” Although search terms such as “anticancer” and “antioxidants” were included, their absence from the final dataset suggested a lack of studies specifically focusing on those plural terms. This indicates that “antioxidant” (singular) was frequently used by authors as a keyword, whereas “antioxidants” (plural) was less common, highlighting the need for more consistent terminology in future research. More studies were needed in skin aging, antibacterial, phytochemistry, DNA repair, selenium, UVA, ferulic acid, genistein, keratinocyte, and tumorigenesis, as they had fewer than 10 associated publications.
When two documents cite the same third source in their reference lists, the so-called bibliographic coupling phenomenon occurs [27]. The strength of this coupling link increases with the number of shared references [28]. In this study, this bibliographic coupling was analyzed using VOSviewer to visualize the relationships between publications, sources, authors, institutions, and countries. In VOSviewer’s visualization, each node represented an entity, such as a keyword, journal, author, or institution, and the links denoted connections based on shared references [29]. The keyword-based network mapping is presented in Figure 4, showing the co-occurrence relationships among frequently used terms in the application of antioxidant in skin cancer treatments.
Figure 4. Keyword Co-Occurrence Network of Antioxidant and Skin Cancer Research Based on Bibliometric Mapping.
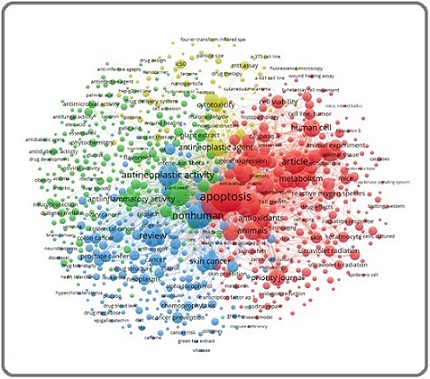
A threshold of at least 10 occurrences per keyword was applied, resulting in the inclusion of 919 keywords. Figure 4 presents the keyword co-occurrence network, where larger nodes indicate higher connectivity with other terms. The analysis revealed six distinct thematic clusters, with the most frequent terms being “apoptosis,” “cancer,” “oxidative stress,” and “antioxidant”. The resulting clusters were classified into six overarching thematic groups: cell biomolecular, drug metabolism, malignancy agent, pharmacological innovation, free radical molecule, and protective agent. Since the two thematic groups of free radical molecules and protective agents only had two keywords respectively, we combined them with the other thematic groups.
These classifications provided a roadmap for future research, as shown in Figure 5. The most frequently identified topic discussed regarding cell biomolecules was apoptosis, along with its intrinsic and extrinsic activation pathways, intracellular metabolism up to the final targets of genetic mutations, and DNA repair mechanisms.
Figure 5. Thematic Clustering of Research Topics in Antioxidant Application for Skin Cancer.
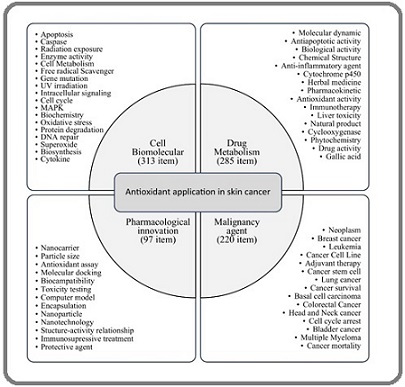
In the second place, we had drug metabolism, where the molecular dynamics of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, the chemical structure and biological activity of drugs, as well as drug toxicity analysis were discussed. This bibliometric review also highlighted cases of malignancy, where almost all types of malignancies were discussed, including cancer survival and mortality rates. Drug innovation was relatively less discussed because it aligned with the technological advancements in pharmacy. Therapeutic novelties led to drug biocompatibility, nanoparticle structures and nanotechnology, encapsulation, computer models, and discussions on immunosuppressive therapy and protective agents.
Discussion
This bibliometric investigation offered a comprehensive depiction of global research output pertaining to the use of antioxidants in the context of skin cancer treatments. The analysis, based on the dataset comprising 990 English publications retrieved from the Scopus database, revealed a steady and notable expansion in scholarly attention over the past three decades, particularly after 2010. The 11.42% annual growth rate and the increasing number of publications, peaking in 2024, highlighted the rising scientific and clinical interest in antioxidant strategies for oncological dermatology. The publications were mostly original research articles, complemented by a substantial number of review papers, indicating that the field has evolved beyond early exploratory studies toward more integrative and synthesizing scholarship that consolidates prior findings and identifies future research directions.” Keywords such as “apoptosis,” “oxidative stress,” and “cancer” emerged as dominant terms, underscoring the central mechanistic roles these processes played in the pathophysiology and therapeutic targeting of skin malignancies.
Country-wide analysis demonstrated that the United States and China were at the forefront of publication outputs, indicating their strong global presences in this research domain. The high degree of international collaboration, particularly evident in European countries, supported the notion of a transnational research effort. Furthermore, the thematic analysis revealed four major research clusters, ranging from cell biomolecular mechanisms to pharmacological innovation. In particular, the key bibliographic clusters included investigations into nanoparticle-based delivery systems, antioxidant pharmacokinetics, and the use of computational modeling in drug design. These findings not only mapped the structural complexity of this research domain but also underscored a shift from descriptive biological studies toward applied, technology-integrated cancer therapeutics. The observed rise in publications and diversified thematic clusters pointed to the evolving conceptual and methodological advancements of antioxidant-based cancer therapy research. Antioxidants, once regarded primarily as nutritional adjuncts, were currently investigated for their role in modulating key intracellular pathways implicated in tumor development and treatment resistance. The fact that apoptosis-related keywords were prominently used reflected a robust body of works examining the molecular crosstalk between antioxidant activity and programmed cell death in skin carcinogenesis. The modulation of signaling axes such as NF-κB and MAPK, and the role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) as both targets and mediators of therapeutic efficacy, suggested that antioxidants are being repositioned as active modulators of oncogenic signaling rather than mere passive radical scavengers.
The emergence of “melanoma” as a prominent topic between 2019 and 2022 could be attributed to the evolving insights into its oxidative biology and therapeutic vulnerabilities. In that period, there was a surge of studies exploring the dual nature of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in melanoma, where ROS acted both as promoters of tumor initiation and targets for therapeutic intervention. An example of this was a review entitled Oxidative Stress in Melanoma, which highlighted how melanoma cells adapted by upregulating antioxidant defenses during later stages, effectively surviving oxidative damage [30]. These complex redox dynamics spurred research to focus more on antioxidant-based strategies.
The prominent use of “apoptosis” in the bibliometric trend from 2012 through 2022 reflected an impactful intersection between redox biology, tumor cell death, and immune-mediated tumor clearance. Having been known to modulate intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS), antioxidants in turn affected the intrinsic and extrinsic apoptosis pathways in solid tumors such as skin cancers. Persistent scholarly interest in “apoptosis” aligned with the discovery that controlled induction of cell death enhanced antitumor immunity, especially through antigen release and dendritic cell activation, making apoptosis a central mechanistic target. Furthermore, the emergence of immunotherapies, such as checkpoint inhibitors targeting PD 1/PD L1, had emphasized the relevance of apoptosis. Studies suggested that apoptotic mechanisms could either synergize with immune-checkpoint blockade by releasing tumor antigens or, conversely, led to tumor cell death if contexts were misregulated [31]. Research into antioxidants thus pivoted on modulating ROS to favor apoptosis of tumor cells while preserving immune effector cells, positioning apoptosis at the nexus of oxidative balance and immune-oncology strategies.
In short, the sustained bibliometric attention to “apoptosis” came from its significance in mechanistically linking antioxidant regulation, tumor cell death, and immunological responses. This underscored its continued relevance in advancing therapies against solid tumors, including skin cancers. It should be noted that the inclusion of ‘apoptosis’ as one of the initial screening keywords may have introduced a selection bias by disproportionately increasing the representation of apoptosis-related studies in the dataset. This methodological choice likely contributed to the prominence of apoptosis in the keyword frequency analysis. Similar outcomes would be expected if alternative mechanistic terms, such as ‘inflammation’ or ‘angiogenesis,’ were included instead. The potential for future bibliometric studies to employ broader, more inclusive keyword strategies is significant, as it can lead to a reduction in bias and an enhancement of thematic generalizability, underscoring the importance of methodological considerations in research.
The transient and minimal presence of the term “tumorigenesis,” as shown by the fact that it appeared only for a single year with very limited frequency, likely reflected the shifting focus of antioxidant-related skin cancer research from broad carcinogenic processes to more specific molecular and therapeutic targets. Traditionally speaking, “tumorigenesis” addressed the initiation and promotion stages of cancer development at a systemic level. However, recent literature emphasized oxidative stress mechanisms and targeted interventions rather than generalized tumor formation. For instance, one study highlighted reactive oxygen species (ROS) as key drivers of DNA damage and mutagenesis, yet they also showcased their dual, context-dependent roles as both tumor initiators and therapeutic agents [32]. This nuanced view encouraged researchers to adopt more precise keywords (e.g., “oxidative stress,” “apoptosis,” “ROS,” “DNA damage”) that better encapsulated specific pathways, reducing the need to use broader terms like “tumorigenesis.”
Another notable trend was the increasing application of nanotechnology and in silico modeling to improve the efficacy and delivery of antioxidant compounds. Over the past five years, nanoparticle systems such as polymeric liposomes and mesoporous silica had been designed for topical or systemic delivery of antioxidants, e.g., curcumin, resveratrol, and polyphenolic extracts, addressing longstanding issues of poor solubility, rapid metabolism, and low bioavailability [33]. These nanocarriers exploited both passive tumor accumulation (via the EPR effect) and active targeting strategies, sometimes employing pH or redox-responsive release mechanisms to maximize drug deposition at the tumor microenvironment while minimizing off-target cytotoxicity. Concurrently, computational methods such as molecular docking and molecular dynamics had become essential tools for high-throughput screening of natural antioxidant molecules against oncogenic targets (e.g., NF κB, Nrf2, BRAF) and for optimizing their structural interactions before experimental validation [34]. The synergy between rational in silico design and finely tuned nanoformulations enabled multifunctional antioxidant therapeutics that combined chemopreventive, cytotoxic, and immunomodulatory effects, situating antioxidants firmly within advanced translational research pipelines for skin cancer. Moreover, the bibliometric data indicated that research had expanded beyond isolated topical applications, integrating antioxidant nanodelivery within broader oncologic contexts, such as combining it with immunotherapies, targeting cancer stem cells, and addressing systemic oxidative loads. This demonstrated a paradigmatic shift toward multi-modal, systems-level cancer treatment strategies driven by oxidative stress, immune function, and cellular signaling networks.
In addition to the bibliometric trends identified in this study, recent clinical trials have highlighted the growing therapeutic relevance of antioxidant-based interventions across various cancer types. For example, a randomized controlled trial by Pashaki et al. (2023) demonstrated that long-term melatonin supplementation significantly alleviated cancer-related fatigue and improved the overall quality of life in breast cancer patients receiving adjuvant therapy. As a naturally occurring antioxidant, melatonin appears to exert both cytoprotective and systemic modulatory effects during cancer treatment [35]. Similarly, a trial by Pakdel et al. (2021) evaluated a polyherbal formulation combining Allium sativum (garlic), Curcuma longa (turmeric), Panax ginseng, and Camellia sinensis (green tea), reporting notable improvements in physical well-being, psychosocial function, and general health status among patients with upper gastrointestinal malignancies. Although these studies focused on non-dermatologic cancers, their findings underscore the translational promise of both endogenous and plant-derived antioxidant therapies within integrative oncology. This emerging clinical evidence complements the bibliometric landscape presented in our study and supports the view that antioxidant research is shifting from mechanistic inquiry toward patient-centered therapeutic innovation.
In reflecting on the scope and limitations of this study, several methodological considerations merit discussion. First, the analysis did not differentiate between studies utilizing natural antioxidants such as plant- derived polyphenols and those examining synthetically produced or chemically modified compounds. Research involving natural compounds is often subject to variability in extraction protocols, purity levels, and dosing units, affecting reproducibility and comparability. Future bibliometric evaluations would benefit from explicitly categorizing these compound types to enhance methodological clarity and analytical precision. Second, the citation analysis did not distinguish between internal citations (citations among publications within the dataset) and external citations (references to studies beyond this dataset). Evaluating such citation dynamics, particularly the extent to which skin cancer antioxidant research draws upon or informs adjacent disciplines, could yield richer insights into the field’s interdisciplinary structure and intellectual evolution.
This bibliometric study offers the first comprehensive mapping of global research trends on the application of antioxidants in skin cancer. The findings reveal a steady increase in publication output, expanding thematic focus on oxidative stress modulation, apoptosis regulation, and advanced therapeutic strategies such as nanocarrier systems and computational modeling. Increasing international collaboration and the emergence of new research clusters further underscore the growing scientific interest in this field. By identifying influential authors, institutions, and keywords, this study provides a strategic roadmap for future investigation. While database limitations and language restrictions remain potential constraints, these findings lay a foundation for integrating mechanistic insights with clinical validation, advancing antioxidant-based strategies into evidence-informed skin cancer prevention and treatment interventions.
Acknowledgements
Funding Statement
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for- profit sectors.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Authors Contribution
L.A. contributed to writing, reviewing, and editing the manuscript; I.B. conceptualized and designed the study; M.A. was responsible for methodology; D.N.A.N. performed data collection; I.I. drafted the original manuscript; S.B. contributed to data visualization; and
M.S. carried out data analysis and interpretation. All authors participated in the literature review, critically revised and approved the final version of the manuscript, and take full responsibility for the integrity and accuracy of the work.
Data Availability
The data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, upon reasonable request.
Study Registration
This study is not registered in any clinical trial or systematic review registry as it does not involve patient data or experimental procedures.
References
- Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL , Soerjomataram I, Jemal A. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians.2024;74(3). CrossRef
- European consensus-based interdisciplinary guideline for melanoma. Part 1: Diagnostics: Update 2022 Garbe C, Amaral T, Peris K, Hauschild A, Arenberger P, Basset-Seguin N, Bastholt L, et al . European Journal of Cancer (Oxford, England: 1990).2022;170. CrossRef
- Advancements and limitations in traditional anti-cancer therapies: a comprehensive review of surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and hormonal therapy Zafar A, Khatoon S, Khan MJ , Abu J, Naeem A. Discover Oncology.2025;16(1). CrossRef
- Oxidative stress and dietary phytochemicals: Role in cancer chemoprevention and treatment Chikara S, Nagaprashantha LD , Singhal J, Horne D, Awasthi S, Singhal SS . Cancer Letters.2018;413. CrossRef
- Exploration of the Use of Natural Compounds in Combination with Chemotherapy Drugs for Tumor Treatment Wu J, Li Y, He Q, Yang X. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland).2023;28(3). CrossRef
- The combination of curcumin and 5-fluorouracil in cancer therapy Wei Y, Yang P, Cao S, Zhao L. Archives of Pharmacal Research.2018;41(1). CrossRef
- Oxidative Stress and Age-Related Tumors Di Carlo E, Sorrentino C. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland).2024;13(9). CrossRef
- Mapping the situation of research on coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19): a preliminary bibliometric analysis during the early stage of the outbreak Zyoud SH , Al-Jabi SW . BMC infectious diseases.2020;20(1). CrossRef
- Exploring Topics in Bibliometric Research Through Citation Networks and Semantic Analysis Mejia C, Wu M, Zhang Y, Kajikawa Y. Frontiers in Research Metrics and Analytics.2021;6. CrossRef
- Cyber parental control: A bibliometric study Altarturi HHM , Saadoon M, Anuar NB . Children and Youth Services Review.2020;116. CrossRef
- Research trends in the bias-based aggression among youth Sánchez-Sánchez AM , Ruiz-Muñoz D, Sánchez-Sánchez FJ . Children and Youth Services Review.2024;158. CrossRef
- Preliminary guideline for reporting bibliometric reviews of the biomedical literature (BIBLIO): a minimum requirements Montazeri A, Mohammadi S, M.Hesari P, Ghaemi M, Riazi H, Sheikhi-Mobarakeh Z. Syst Rev .2023;12:1-10. CrossRef
- A bibliometric and content analysis of technological advancement applications in agricultural e-commerce Altarturi HHM , Nor ARM , Jaafar NI , Anuar NB . Electronic Commerce Research.2025;25(2). CrossRef
- Prolonged grief disorder: A bibliometric analysis Koukopoulos A, Neimeyer RA . Death Studies.2024;48(2). CrossRef
- bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis Aria M, Cuccurullo C. Journal of Informetrics.2017;11(4). CrossRef
- Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping Eck NJ , Waltman L. Scientometrics.2010;84(2). CrossRef
- Therapeutic potential of resveratrol: the in vivo evidence Baur JA , Sinclair DA . Nature Reviews. Drug Discovery.2006;5(6). CrossRef
- Flavonoids: antioxidants or signalling molecules? Williams RJ , Spencer JPE , Rice-Evans C. Free Radical Biology & Medicine.2004;36(7). CrossRef
- ICRP publication 118: ICRP statement on tissue reactions and early and late effects of radiation in normal tissues and organs--threshold doses for tissue reactions in a radiation protection context Stewart F. A., Akleyev A. V., Hauer-Jensen M., Hendry J. H., Kleiman N. J., Macvittie T. J., Aleman B. M., et al . Annals of the ICRP.2012;41(1-2). CrossRef
- Cancer prevention by tea: animal studies, molecular mechanisms and human relevance Yang CS , Wang X, Lu G, Picinich SC . Nature Reviews. Cancer.2009;9(6). CrossRef
- Distribution and biological activities of the flavonoid luteolin López-Lázaro M. Mini Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry.2009;9(1). CrossRef
- Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of skin disease Bickers DR , Athar M. The Journal of Investigative Dermatology.2006;126(12). CrossRef
- Ferulic Acid: therapeutic potential through its antioxidant property Srinivasan M, Sudheer AR , Menon VP . Journal of Clinical Biochemistry and Nutrition.2007;40(2). CrossRef
- Inhibition of carcinogenesis by tea Yang CS , Maliakal P, Meng X. Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology.2002;42. CrossRef
- Melatonin: Nature's most versatile biological signal? Pandi-Perumal S. R., Srinivasan V., Maestroni G. J. M., Cardinali D. P., Poeggeler B., Hardeland R.. The FEBS journal.2006;273(13). CrossRef
- UV-induced skin damage Ichihashi M., Ueda M., Budiyanto A., Bito T., Oka M., Fukunaga M., Tsuru K., Horikawa T.. Toxicology.2003;189(1-2). CrossRef
- Analysis of direct citation, co-citation and bibliographic coupling in scientific topic identification Kleminski R, Kazienko P, Kajdanowicz T. Journal of Information Science.2022;48(3). CrossRef
- Science Forec Moral-munoz JA , López-herrera AG , Herrera-viedma E, Cobo MJ . 2019;:159-85.
- How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines Donthu N, Kumar S, Mukherjee D, Pandey N, Lim WM . Journal of Business Research.2021;133. CrossRef
- Oxidative Stress in Melanoma: Beneficial Antioxidant and Pro-Oxidant Therapeutic Strategies Becker AL , Indra AK . Cancers.2023;15(11). CrossRef
- Immune Checkpoints and Cellular Landscape of the Tumor Microenvironment in Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer (NMSC) Mousa AM , Enk AH , Hassel JC , Reschke R. Cells.2024;13(19). CrossRef
- Role of ROS‑mediated autophagy in melanoma (Review) Zhang X, Li H, Liu C, Yuan X. Molecular medicine reports.2022;26(4). CrossRef
- Elucidation of anti-human melanoma and anti-aging mechanisms of compounds from green seaweed Caulerpa racemosa Wicaksono D, Taslim NA , Lau V, Syahputra RA , Alatas AI , Putra PP , Tallei TE , et al . Scientific Reports.2024;14(1). CrossRef
- Molecular docking studies for NPACT ligands for the treatment of melanoma skin cancer Premkumar B., Yesuraj SR , Mohan S, Chandran S. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Chemistry and Analysis.2025;11(1). CrossRef
- A Randomized, Controlled, Parallel-Group, Trial on the Long-term Effects of Melatonin on Fatigue Associated With Breast Cancer and Its Adjuvant Treatments Sedighi Pashaki A, Sheida F, Moaddab Shoar L, Hashem T, Fazilat-Panah D, Nemati Motehaver A, Ghanbari Motlagh A, et al . Integrative Cancer Therapies.2023;22. CrossRef
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright
© Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Care , 2025
Author Details
How to Cite
- Abstract viewed - 0 times
- PDF (FULL TEXT) downloaded - 0 times
- XML downloaded - 0 times